Last Updated on December 16, 2025 by gaojie
If you typed “can you AI enhance videos” into Google, you’re probably not looking for a robot speech about “the future of AI.”
You want a straight answer:
- Can AI make my blurry video look better?
- Can it upscale to 1080p or even 4K?
- Will it fix noise, low light, and shaky footage?
- Or will it just make everything look weird and plastic?
Let’s do this like a friend who doesn’t sell miracles.
The honest answer: yes, you can AI enhance videos — but only if the problem is “fixable”
AI video enhancement works best when your video has real picture information that’s just hidden under:
- low resolution (480p / 720p)
- grain / noise
- mild blur
- compression artifacts
- dull lighting or weak colors
AI struggles when your video is missing information entirely, like:
- heavy motion blur (fast movement + slow shutter)
- giant blocks of compression (old WhatsApp clips, re-uploaded memes)
- face details that were never captured (super zoomed, super dark)
- extreme overexposure (pure white areas)
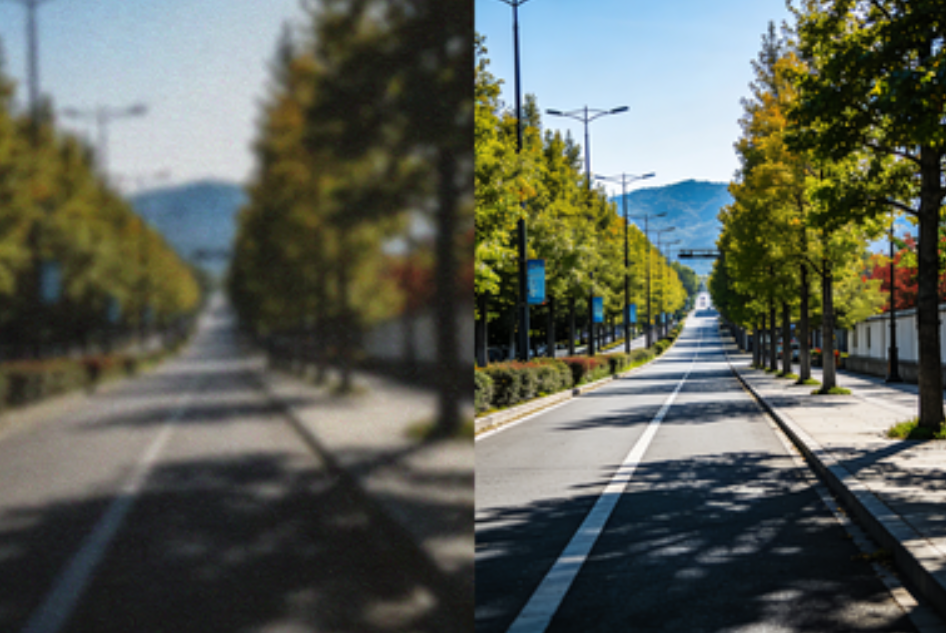
A good AI video enhancer can make your clip cleaner and sharper, and sometimes it can upscale video to HD or 4K in a way that looks real. But it can’t “recreate the truth” like a time machine.
What “AI video enhancement” actually does (in normal human language)
When people say enhance video quality, they usually mean a mix of these:
Upscale (increase resolution)
This is the “make my 480p video look like 1080p/4K” part.
A real AI video upscaler doesn’t just stretch pixels. It tries to rebuild detail by learning patterns (edges, textures, faces, hair, text).
Denoise (remove grain)
This is huge for night footage: street lights, concerts, indoor birthday videos, old phones.
Good denoise removes the “sand” without melting skin into wax.
Deblur / sharpen (carefully)
This can help mild blur. But too much sharpening can create halos or crunchy edges.
Improve color and contrast
Many tools auto-boost brightness, contrast, and saturation to make clips “pop.”
Frame rate tricks (slow motion / smoother motion)
Some enhancers can generate extra frames for smoother slow motion or higher frame rates. (This is not magic either—it can create odd motion if the scene is complex.)

Why this keyword needs a real guide (not another marketing page)
If you look at the search results for “can you AI enhance videos,” you’ll notice a pattern:
- Lots of tool pages saying “one click, perfect 4K.”
- Lots of listicles with 10–20 tools.
- Lots of basic tutorials that don’t explain what to expect.
So the blog that gets clicks (and keeps readers) is the one that does two things:
- Sets expectations clearly
- Gives a simple workflow that actually works
That’s what this guide is.
The “Worth It?” test: should you even try to AI enhance your video?
Here’s a fast checklist. If you say “yes” to at least 2–3 of these, AI enhancement is usually worth trying.
AI enhancement is likely to help if:
- Your video is 480p or 720p, but not completely destroyed.
- You see grain/noise, especially in dark areas.
- Faces are visible but just a little soft.
- The video looks “flat” (low contrast, dull colors).
- The clip is important (family memory, school project, content you want to post).
AI enhancement may NOT help much if:
- The video is a “blocky mess” (heavy compression).
- Everything is smeared during movement (strong motion blur).
- It’s too dark to see anything.
- It’s a screen recording of a screen recording (double compression).
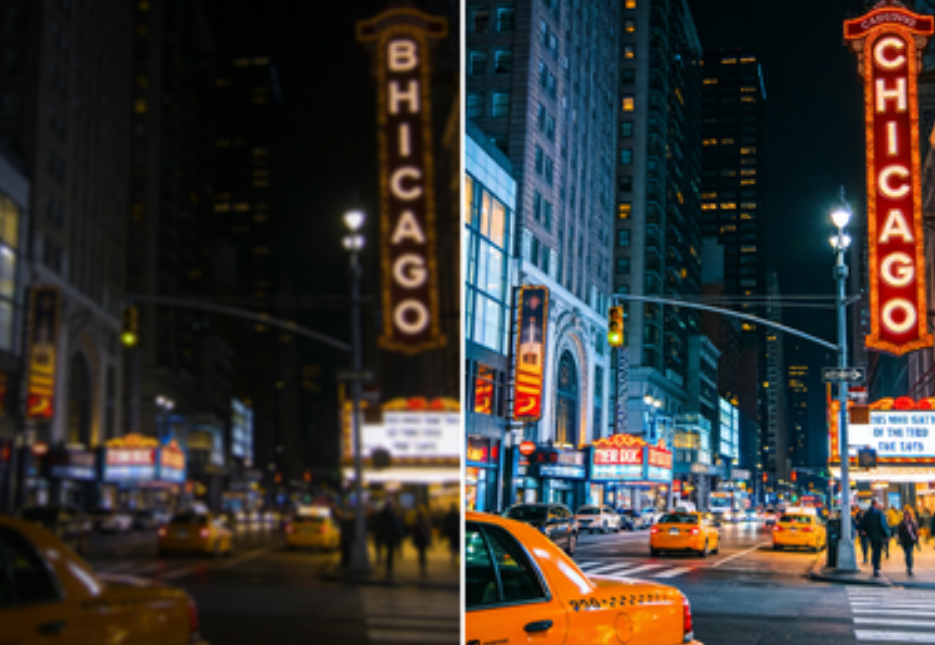
What results should you expect (realistic before/after)
When AI enhancement works, the best improvements usually look like this:
- edges look cleaner (hair, clothing outlines, text)
- noise is reduced (especially in shadows)
- faces look clearer (but not suddenly “Hollywood”)
- the video looks more modern and less “old phone”
When AI enhancement goes wrong, you’ll see:
- plastic skin
- “painted” textures (grass, walls, hair)
- weird flicker between frames
- crunchy over-sharpened edges
Your goal is not “perfect.” Your goal is better + natural.
A simple workflow to AI enhance videos (the 10-minute version)
This is the workflow I recommend because it prevents the most common mistake: doing everything at once and ruining the video.
Step 1: Start with the smallest problem
Pick the main issue:
- grainy? → denoise first
- soft/low-res? → upscale + mild sharpen
- dull? → color/contrast
Trying to fix everything in one pass often creates artifacts.
Step 2: Enhance a short sample first
Don’t process a 10-minute clip right away.
Take a 10–20 second section that includes:
- a face (if there is one)
- movement
- dark areas (noise shows up here)
If the sample looks good, then process the full video.
Step 3: Compare on the right screen
Phone screens hide problems. If possible, check on:
- laptop/desktop
- full screen view
- pause on tricky frames (motion + shadows)
Step 4: Stop early if it starts looking fake
A slightly soft but natural video is better than a crispy, fake one.
How to enhance video quality online with GStory (simple + beginner-friendly)
If you want an online AI video enhancer that doesn’t require downloading software, GStory’s Video Enhancer is built for the “upload → process → download” style workflow.
Here’s the basic process (and why it’s beginner-friendly):
1) Upload your clip
GStory’s page supports common formats like MP4, WEBM, MOV, M4V, MKV, and even GIF, with limits shown directly on the upload area (up to 500MB and 10 minutes).
2) Process, then download
The tool is designed around a short, two-step flow: upload, then process and download. It also mentions batch upload, which is handy if you’re enhancing multiple clips for a project.
3) What it tries to improve
On the page, GStory describes improvements like:
- upscaling low-resolution footage
- reducing noise and motion blur
- one-click enhancement up to 4K at 30fps
Online vs desktop enhancers: which one should you choose?
Both can work. The best choice depends on your situation.
Choose an online video enhancer if you want:
- fast results
- no installation
- beginner-friendly workflow
- easy sharing and quick exports
Choose a desktop AI video enhancer if you need:
- deep control over settings
- heavy restoration work
- offline processing for privacy reasons
- lots of trial-and-error with parameters
Most people searching “can you AI enhance videos” are beginners who just want something that works quickly. That’s why online tools do well for this query.
Common mistakes that make AI-enhanced videos look worse
Mistake 1: Upscaling a clip that’s already “fake sharp”
Some videos (especially from social apps) already have sharpening baked in. Upscaling those can create nasty halos.
Mistake 2: Over-denoising faces
Noise reduction can remove detail. If a tool is too aggressive, skin turns into a smooth mask.
Mistake 3: Ignoring motion blur
AI can’t fully fix motion blur. It may sharpen the blur, which looks strange.
Mistake 4: Judging the result only on your phone
Phone screens are forgiving. Always check at least once on a larger screen.
The “quality checklist” I use after enhancement
After you enhance video quality, do a quick scan:
- Faces: do they look natural, or “AI-painted”?
- Edges: any halos around people or objects?
- Shadows: did noise reduce without turning into mush?
- Motion: any flicker between frames?
- Text/logos: did they get clearer or weirdly distorted?
If you spot issues, the solution is usually simple: dial it back (less sharpening, less denoise, or don’t force a huge jump to 4K).
A quick note on what’s changing in 2025
One reason this topic is exploding is that major platforms are also leaning into “AI upscaling.” For example, YouTube has been reported to be rolling out AI-powered “super resolution” style upscaling for lower-resolution videos, with plans to improve quality beyond SD/HD over time.
That doesn’t mean every clip becomes perfect. But it does mean AI enhancement is becoming mainstream—and the tools are getting better.
FAQ: quick answers people actually want
Can AI enhance videos for free?
Sometimes, yes—many tools offer free previews, credits, or limited exports. Always check the limits (watermark, resolution caps, file size, and export rules). GStory’s ecosystem includes a free account model and a credits approach on its pricing pages.
Can AI upscale a video to 4K?
Some tools can output 4K, but output resolution is not the same as “real detail.” A good AI upscaler can improve perceived detail, especially from 480p/720p sources. GStory’s page explicitly mentions one-click upscaling up to 4K at 30fps.
Can AI unblur a video?
Mild blur: often yes (a bit). Heavy motion blur: usually no. Be careful—many “unblur” results are just sharpening.
Is it safe to upload videos to an online enhancer?
It depends on the provider and your content. For sensitive videos, read the tool’s policies and avoid uploading anything you wouldn’t want stored. (Even if you trust a tool, good privacy habits are smart.)
Final thoughts: the best way to win with AI video enhancement
So… can you AI enhance videos? Yes.
But the real skill is knowing what to ask AI to do, and when to stop.
If you do these three things, you’ll get the best results most of the time:
- Start with a short sample clip
- Fix the biggest problem first (noise, resolution, or color)
- Choose “natural improvement” over “aggressive AI makeover”
And if you want the simplest beginner path, an online workflow like the one on GStory’s Video Enhancer page is designed for exactly that: upload, process, download—no complicated editing steps.

Leave a Reply